Use cable fault tester to accurately detect cable faults
With the increasing demand for electricity in cities and rural areas, power cables are widely used as connecting circuits and transmission tools. The construction and transformation of power grids have increased the application of power cables year by year and the scope of application has become wider and wider. However, the difficulty of connecting power cables, complex construction processes and construction environments make cable faults occur from time to time. Therefore, power supply companies and relevant departments pay more and more attention to the analysis of the causes of power cable faults and the research and application of solutions.
Cable faults are mainly divided into the following types: Open circuit faults, Low resistance faults, and High resistance faults
Open circuit faults: refers to the resistance value between cables or cables to the ground is within the specified value range, but the actual working voltage cannot be transmitted to the terminal or although some voltage is transmitted to the terminal, there is almost no load capacity. Common phenomena include short circuit and open circuit.
Low resistance fault: When the insulation between cables is damaged or the insulation between cables and the ground is damaged, the insulation resistance of the cable will inevitably decrease. When the insulation resistance of the cable is smaller than ten times the characteristic impedance of the cable, we call this fault a low resistance fault, which may cause excessive current, overheating of the wire, and even fire.
High resistance fault: When the insulation resistance between cables or between cables and the ground is much lower than the normal value, but larger than ten times the characteristic impedance of the cable, we call this cable fault a high resistance fault. This situation will cause local heating of the cable, insulation breakdown and other problems.
Common solutions to cable faults include the following: Time domain reflection method (TDR), Impulse high voltage flashover method, Low voltage pulse reflection method, and Bridge method.
Time domain reflection method (TDR): Determine the fault location in the cable by sending a pulse signal and measuring the time and strength of the reflected signal. This method utilizes the transmission line characteristics in the cable and is suitable for detecting undesirable conditions such as open circuit, short circuit, low resistance and high resistance in the cable.
Impact high-voltage flashover method: By applying high voltage to the cable, the fault point is caused to produce discharge phenomenon (flashover), thereby locating the fault point. When the voltage reaches a certain level, the air or medium around the fault point is broken down, forming an arc phenomenon, and producing obvious sound or light phenomenon, thereby locating the fault point. It can be used to find high-resistance fault points, such as cable insulation breakdown, cable sheath damage, etc.
Low-voltage pulse reflection method: By transmitting a low-voltage pulse signal to the cable, the fault point is located by using the reflection of the signal or generating a specific response at the fault point. When the pulse signal reaches the fault point, it will generate reflection or indicate a specific signal, thereby locating the fault point. It is suitable for detecting low-resistance fault points, such as short circuit, open circuit, poor contact, etc. of the cable.
Bridge method: Using the principle of circuit balance, by adjusting the values of certain components in the bridge circuit to make the circuit present a balanced state, the parameters of the component to be tested can be determined by measuring the conditions when balanced. The advantages of the bridge method are simple, convenient and high-precision testing, but it is not suitable for detecting high-resistance faults and flashover faults, and the cable length must be known before the test to measure.
Different methods solve different cable fault problems, so we need a cable fault test system with different units to solve all cable fault problems. TFN cable fault tester provides a solution for testing cable faults.
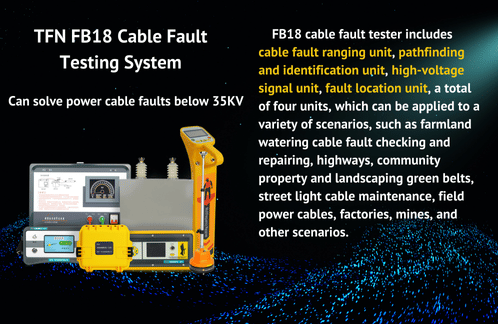
TFN cable fault tester mainly consists of four units, namely: Fault distance measurement unit, Path finding and identification unit, Fault location unit, and High-voltage signal unit. So, how to use the different units of the cable fault tester to accurately detect cable faults?
Step 1: Before testing, first understand the basic situation of the cable and find out the cause of the fault. The approximate length, type, usage time, previous faults, whether there are joints in the middle of the cable, cable laying method, etc.
Step 2: Make sure that both ends of the cable are disconnected from other lines and keep them in a safe state without electricity.
Step 3: Before connecting the cable, connect each phase line of the cable to the ground with a short-circuit line for discharge. When discharging, one end of the short-circuit line must be grounded first, and the other end must be connected to each phase line of the cable for discharge. (Discharge first and then operate)
Step 4: Use the fault distance measuring unit to test the full length of the cable, low-resistance short-circuit fault, and disconnection fault distance through the low-voltage pulse reflection method; then use the high-voltage flashover method to test the fault distance of the high-resistance fault; display the waveform on the screen through sampling and automatically judge the distance and display the fault type. Note: Low-voltage pulses can directly test the low-resistance or disconnection fault of the fault distance, and high-voltage flashover is generally required for verification testing and fault point location.
Step 5: Use the path finding and identification unit to use the underground pipeline detector to perform detailed path search and find the detailed path of the cable with the measured fault distance
Step 6: Use the high-voltage signal unit to apply a high-voltage pulse signal to the cable fault phase through a light high-voltage signal generator, so that the cable fault point can generate intermittent discharge, thereby performing fault point distance test and precise location.
Step 7: Use the fault location unit to perform precise location through two modes: step voltage and acoustic magnetic location. The step voltage mode mainly tests the single-phase grounding fault under the state of direct buried low voltage unarmored cable; the acoustic magnetic fixed point method can make subjective judgments on the cable distance and position according to the size of the discharge sound at the fault point of the tested cable.

TFN cable fault tester can measure high and low resistance faults of all cables below 35KV, has a wide range of adaptability, and has user-friendly software and tutorials. It has a high success rate of fault detection, high test accuracy, and convenient testing, so you can choose it with confidence.
Operation tutorial video link:
https://youtu.be/SDFNZ1eXHcs?si=kAcHJjq3R1z2aGj9
If you are interested in TFN cable fault tester, please contact TFN sales team:
Email: info@tfngj.com
WhatsApp: +86-18765219251
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/tfnfate/
