How to use underground pipeline detectors to maintain urban underground pipeline networks?
Underground pipelines are an important part of urban infrastructure and are the "lifeline" to ensure urban operation and development. However, due to insufficient construction scale, insufficient data preservation, and inadequate daily management, the accurate detection of underground pipelines is becoming increasingly difficult. To this end, this article introduces the classification, material, specifications and laying methods of common underground pipelines in detail, and introduces the detection methods of underground pipelines.

Urban underground pipelines refer to pipelines and their ancillary facilities for water supply, drainage, gas, heat, electricity, communications, radio and television, industry, etc. in the city. They are important infrastructure and "lifelines" to ensure the operation of the city. However, in recent years, with the increasing frequency of urban construction, problems such as unreasonable pipeline design, incomplete pipeline cleaning, missing data preservation, and inadequate daily maintenance have generally appeared in various places, resulting in the aging, density, and disorder of underground pipelines becoming more and more serious. In some cities, pipeline leakage, rainstorm waterlogging, and third-party construction digging pipelines have occurred, disrupting the order of urban operation and seriously threatening the safety of people's lives and property.
Due to the different materials, specifications, and transmission materials of underground pipelines, their physical properties are significantly different from those of the surrounding media. Using geophysical methods to detect underground pipelines has become an effective technology, among which the most commonly used are electromagnetic method and ground penetrating radar method. The main electromagnetic methods are: electromagnetic induction method and high-density resistivity method. The electromagnetic induction method is suitable for metal pipeline detection, and the high-density resistivity method and ground penetrating radar method are suitable for non-metallic pipeline detection. Underground pipeline detectors mainly use the principle of electromagnetic induction to detect metal pipelines. Metal pipelines mainly include steel pipes, galvanized steel pipes, cast iron pipes, ductile iron pipes, and metal cables made of copper and aluminum. Most of these pipes have good electrical conductivity and magnetic conductivity, and have significant differences in physical properties from the surrounding media. The principle of electromagnetic induction can be used to quickly and effectively screen underground pipelines.
The pipeline detector made by electromagnetic induction principle is one of the most widely used underground pipeline detectors. Its principle is: the transmitter generates electromagnetic waves and transmits the transmission signal to the underground metal pipeline to be detected through different transmission connection methods. After the underground metal pipeline senses the electromagnetic waves, an induced current is generated on the surface of the underground metal pipeline. The induced current will propagate far away along the metal pipeline. During the propagation of the current, it will radiate electromagnetic waves to the ground through the underground metal pipeline. In this way, when the underground pipeline detector receiver detects on the ground, it will receive electromagnetic wave signals on the ground just above the underground metal pipeline. The position and direction of the underground metal pipeline can be determined by the changes in the strength of the received signal.
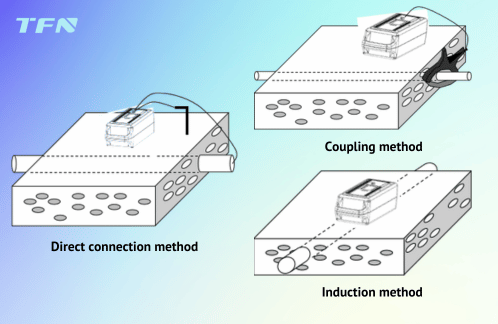
The electromagnetic induction method is generally divided into active source method and passive source method. In practice, the active source method is more widely used. Further subdivided according to the detection method, the active source method can be divided into direct connection method, coupling method and induction method.
Direct connection method: It is the best detection method. The red end of the transmitter output line is directly connected to the exposed metal part of the pipeline. Do not connect it to the live running line. The other end is grounded. This method produces the strongest signal and the longest propagation distance. It is suitable for low-frequency and radio frequency working states.
Coupling method: When it is not possible to directly connect to the pipeline to be tested, a coupling clamp can be used to detect by coupling method. This method can select the transmission frequency according to the actual situation on site: low frequency, radio frequency. When the near end and the far end of the underground pipeline are well grounded and form a loop, the low frequency is used at this time; if the grounding at both ends is not good, the loop resistance is too large, or the low-frequency signal cannot be coupled, then use radio frequency to test. There is no fixed principle for selecting frequency. The basic principles of frequency selection are given below: For high-resistance pipelines (such as communication cables, pipelines with anti-corrosion layers and cast iron pipes), use radio frequency. It should be noted that the higher the frequency, the easier it is for the signal to be sensed on other pipelines, and the shorter the signal propagation distance. For general pipeline and cable detection, use medium frequency and high frequency. These frequencies have a long propagation distance and will not sense too many signals on other pipelines. Low frequency is suitable for long-distance tracking. Low-frequency signals have a long propagation distance and will not be induced on other pipelines. Low-frequency signals are also suitable for long-distance and well-insulated transmission pipelines.
Induction method: In some cases, it is impossible for the operator to approach the cable for direct connection or use a coupling clamp to apply a signal. At this time, the built-in induction antenna of the transmitter can be used to transmit the output signal, and the signal can be induced to the underground cable under test for positioning detection. First, place the transmitter directly above the ground of the cable. The transmitter should be placed in the direction that the indicator line on the transmitter panel is consistent with the direction of the pipeline path. Then use the receiver on the ground above the pipeline to detect the location of the underground pipeline. This method can only use radio frequency but not low frequency, and both ends of the pipeline under test must have good grounding, that is, the pipeline under test must have a good loop.
Method |
Signal transmission method |
Whether to contact the pipeline |
Detection advantages |
Detection disadvantages |
Applicable pipeline conditions |
Direct connection method |
Connect one or both ends of the antenna to the exposed point of the pipeline |
Yes |
Strong signal, fast speed, high precision, simple operation, able to distinguish adjacent pipelines |
The target pipeline must have an exposed point |
Small-diameter pipelines |
Coupling method |
Apply the signal to a special clamp, and then clamp the clamp on the target pipeline |
Yes |
The target pipeline must have an exposed point and its diameter must be smaller than the clamp diameter |
||
Induction method |
Use the alternating coil to excite the secondary field |
No |
Simple operation, fast speed |
The accuracy is generally lower than the direct connection method and coupling method, with poor anti-interference ability and shallow detection depth |
Metal pipelines with shallow burial depth, blind pipelines, and determining pipeline directions |
In practical applications, the use of underground pipeline detectors to maintain urban underground pipelines requires a complete and scientific operating process, which can significantly improve the management and maintenance efficiency of urban underground pipelines and reduce unnecessary excavation and damage.
1. Preliminary preparation: Collect underground pipeline drawings, analyze geographic information systems (GIS), and understand the layout and history of underground pipelines.
2. Make a plan: clarify the detection area and specific pipeline types, understand the risks of the operation area, and make a safe operation plan
3. Equipment selection: Select a suitable detector according to the specific pipeline type. The underground pipeline detector is suitable for metal pipelines.
4. On-site detection: Select the appropriate detection technology according to the situation of the target pipeline. (Direct connection method/coupling method/induction method)
5. Data collection and analysis: Establish a 3D model of the underground pipeline according to the pipeline direction and burial depth data detected by the underground pipeline detector.
6. Pipeline maintenance: Develop a specific maintenance plan based on the fault point situation and 3D model measured by the underground pipeline detector. During construction, excavate, repair or replace the pipeline according to the plan to ensure that other pipelines are not damaged.
7. Record and update: store new detection data and maintenance records in the urban underground pipeline management system, and update drawings and GIS data to ensure the timeliness and accuracy of information
8. Continuous monitoring: establish regular inspection mechanisms and emergency response mechanisms.
For a long time, underground pipelines have been like the blood vessels of a city. Their safety, stability, reliability and operating efficiency are related to people's normal work and life. Once a problem occurs, it will directly disrupt the order of urban operation and affect the production and life of the people. Therefore, it is very important to use reasonable and effective detection methods to detect them and find out the location, burial depth and spatial distribution of underground pipelines. TFN T6000 underground pipeline detector supports multiple optional frequencies and can detect up to a depth of 20 meters, quickly locate the pipeline position, and determine the direction and depth of underground metal pipelines.

If you are interested in the TFNT6000 underground pipeline detector, please contact the TFN sales team:
Email: info@tfngj.com
WhatsApp: +86-18765219251
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/tfnfate/
