Description of different event types in OTDR
OTDR (Optical Time Domain Reflectometer) is a commonly used test equipment in the field of optical fiber communications. It locates and analyzes various problems in optical fiber lines by measuring the reflected and scattered light signals in the optical fiber. In the test results of OTDR, different event types are displayed on the optical fiber curve chart with specific symbols and parameters. These events provide important reference information for the maintenance and optimization of optical fiber lines. The following is a detailed description of common event types in OTDR.
1. Span start and span end 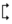 /
/ 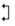
The span start and end are used to mark the start and end positions of the optical fiber span. The span start usually defaults to the first event of the tested optical fiber (such as the first connector of the OTDR), but users can also set other events as the span start as needed. The span end defaults to the last event of the tested optical fiber (fiber end event), and users can also set other events as the span end. These two marks help users focus on analyzing specific spans.
2. Start event and end event  /
/ 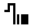
The start event is the first event of the tested fiber, usually the first connector of the OTDR. The end event usually marks the end of the test area, which may be the end of the fiber or other specific locations. These two events provide important reference information for fiber testing.
3. Non-reflective event 
Its characteristics are a sudden decrease in the Rayleigh backscattering signal level and a discontinuous slope of the curve signal decline. This event is usually caused by connectors, macrobends or microbends or other non-reflective losses in the fiber. In the application, non-reflective events will display loss values but not reflectivity. When the loss value exceeds the set threshold, the application will indicate a non-reflective fault.
4. Reflective event (may be an echo) 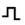
Reflective events appear as spikes in the fiber curve, caused by sudden changes in the refractive index. This event may indicate a connector, mechanical joint, poor quality fusion joint or crack, etc. In the application, reflective events will display loss values and reflectivity. It should be noted that reflective spikes may cause the detector to saturate, thereby increasing the blind area. When the reflectivity or connector loss exceeds the set threshold, the application will indicate a reflective fault.
5. Macrobend Events 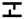
Macrobend events are identified by comparing the difference in loss values of events at the same location at different wavelengths (such as 1310nm and 1550nm). This method helps distinguish macrobends from other types of losses. When the loss at the longer wavelength is greater and the difference between the two loss values is greater than the specified difference, the device will confirm and display it as a macrobend event.
6. Gain Events 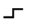
Gain events are relatively rare in fiber optic communications and may be caused by special fiber connectors or connection techniques. Gain events indicate connectors with significant gain, which is generated by joining two fiber sections with different backscattering characteristics.
7. Fiber Segments 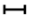
Fiber segments represent the portion of fiber without events. The sum of all fiber segments within the entire fiber curve is equal to the total fiber length. In the application, fiber segments display loss values but not reflectivity. Users can calculate attenuation values by dividing the loss value by the length of the fiber segment.
8. Merged Events 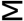
Merged events are formed when multiple events overlap or approach each other on the OTDR curve. The total loss and related reflectivity information of these events are displayed. In the application, merged events display the reflectivity of all merged events and the maximum reflectivity of the sub-events.
9. Testing and Pass/Fail Judgment
The pass/fail test is judged based on preset thresholds and test conditions, which should be set according to the specific application scenario and fiber performance requirements. False positives or false negatives may occur when performing pass/fail testing. Test conditions include testing all event types, testing only selected event types, or testing no event types. When testing all event types, the event status is determined based on the comparison of event loss with the threshold. This helps users understand the overall performance and potential problems of the fiber line.
In short, by understanding and analyzing the different event types in the OTDR, users can more accurately locate and solve problems in the fiber line, thereby improving the stability and reliability of the fiber communication system.
The TFN RM7 OTDR has significant characteristics in representing different event types. It can accurately detect non-reflective events, reflective events, macrobend events, etc. in the optical fiber, and provide detailed loss values and reflectivity. This brings users accurate fiber fault detection and location capabilities, which helps to quickly troubleshoot and solve problems in fiber communications.
If you are interested in the TFN RM7 OTDR, please contact the TFN sales team:
Email: info@tfngj.com
WhatsApp: +86-18765219251
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/tfnfate/
